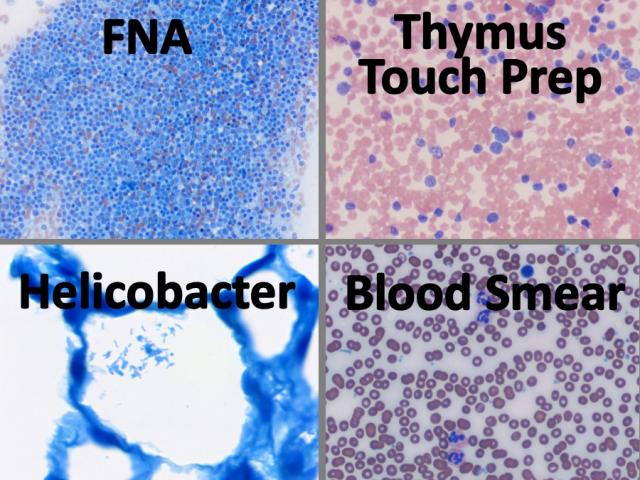
Differential Stain Kit
(use: Hematological Staining & Special Stain for Helicobacter pylori)
Differential staining of peripheral blood smears, touch imprints, fine needle aspirations (FNA), bone marrow biopsy aspirations, as well as detecting Helicobacter pylori sp. in GI tissue. Can be used for smears, touch imprints and tissue sections. This is a modification of the Wright Giemsa Stain technique using aqueous based stain solutions and a methanol fixative. Procedures for both monochromatic and polychromatic versions of the Differential Stain are provided.
-
-
- Shelf Life is 2 years from date of manufacture.
-
Tech Memo 1: Differential Stain Kit for Smears & Touch Imprints
DIFFERENTIAL STAIN KIT FOR SMEARS & TOUCH IMPRINTS INCLUDES:
| Part 9112B | ||
| Solution A: | Xanthene Stain | 500ml |
| Solution B: | Thiazine Stain | 500ml |
| Solution C: | Fixative | 500ml |
Individual stain solutions may be available for purchase under separate part numbers.
Additionally Needed:
| Xylene, ACS | Part 1445 |
For storage requirements and expiration date refer to individual bottle labels.
APPLICATION:
Newcomer Supply Differential Stain Kit, a modification of the Wright Giemsa Stain, uses a methanol fixative and aqueous based stains to provide a rapid 3-step process for differential assessment of: peripheral blood smears, touch imprints, fine needle aspirations (FNA), bone marrow biopsy aspirations, and detecting microorganisms.
METHOD:
Solutions: All solutions are manufactured by Newcomer Supply, Inc.
All Newcomer Supply Stain Kits are designed to be used with Coplin jars filled to 40 ml following the staining procedure provided below. Some solutions in the kit may contain extra volumes.
STAINING PROCEDURE:
-
- Prepare within an accepted time frame, a well-made blood smear, touch imprint, FNA smear or bone marrow aspiration smear/film per your laboratories protocol, with a focus on uniform cell distribution.
- Allow slides to thoroughly air-dry prior to staining.
- Dip dried slides in Solution C: Fixative 5-10 times, one second per dip. Allow excess fixative to drain.
- Dip in Solution A: Xanthene Stain 5 times, one second per dip. Allow excess solution to drain.
-
- See Procedure Notes #1, #2 and #3.
-
- Quickly rinse slides with distilled water.
- Dip slides in Solution B: Thiazine Stain 5 times, one second per dip. Allow excess solution to drain.
- Rinse slides quickly in distilled water.
- Allow slides to air-dry, then examine microscopically.
- If coverslip is preferred, allow slides to air-dry; dip dried slides in xylene and coverslip with compatible mounting medium.
RESULTS:
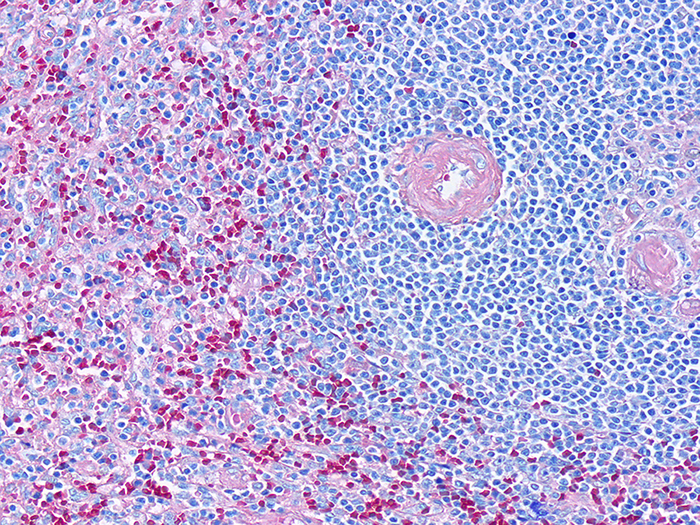
| Erythrocytes: | Pink to yellowish-red |
| Platelets: | Violet or purple granules |
Granulocytes
| Neutrophils: | Nucleus – Dark blue to violet |
| Cytoplasm – Pale pink | |
| Granules – Purple to lilac | |
| Eosinophils: | Nucleus – Blue |
| Cytoplasm – Blue | |
| Granules – Red to red-orange | |
| Basophils: | Nucleus – Purple or dark blue |
| Granules – Dark purple |
Mononuclear Cells
| Monocytes: | Nucleus – Violet |
| Cytoplasm – Sky blue | |
| Lymphocytes: | Nucleus – Violet |
| Cytoplasm – Dark blue | |
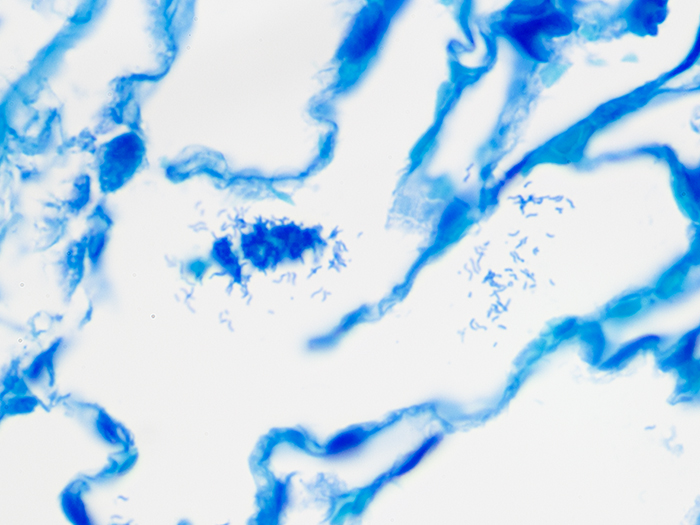
| Bacteria/microorganisms: | Deep blue in varying shapes |
| Muscle and collagen | Pale Pink |
| Nuclei | Blue/violet |
| Cytoplasm | Varying shades of light blue |
PROCEDURE NOTES:
-
- The division of stains in this kit gives the user the advantage of varying dips in Solutions A and B to produce different degrees of shading and intensity. However; never use fewer than three dips of one full second each.
- If more intense stain is desired, increase dips in Solutions A and B.
-
- To increase eosinophilic staining; increase dips in Solution A.
- To increase basophilic staining; increase dips in Solution B.
-
- If a paler stain is desired; decrease dips in Solutions A and B.
- If using a xylene substitute, closely follow the manufacturer’s recommendations for coverslipping application.
REFERENCES:
-
- Bain, B.J. “Bone Marrow Aspiration”. Journal of Clinical Pathology 54 (2001): 657-663.
- Cox, Charles. “Accuracy of Intraoperative Imprint Cytology for Sentinel Lymph Node Evaluation in the Treatment of Breast Carcinoma.” Cancer Cytopathology1 (2005): 13-20.
- “Guidelines of the Papanicolaou Society for Fine-Needle Aspiration Procedure and Reporting.” Diagnostic Cytopathology 17 (1997): 239-247.
- McPherson, Richard and Matthew Pincus. Henry’s Clinical Diagnosis and Management by Laboratory Methods. 22nd ed. Philadelphia: Elsevier Saunders, 2011. 522-535.
- Thompson, Samuel Wisley, and Ronald D. Hunt. Selected Histochemical and Histopathological Methods. 2nd ed. Springfield, IL: Thomas, 1966. 756-762.
- Modifications developed by Newcomer Supply Laboratory.
Tech Memo 2: Differential Stain Kit, Helicobacter Pylori, sp. in Tissue Sections
DIFFERENTIAL STAIN KIT, HELICOBACTER PYLORI, SP IN TISSUE SECTIONS INCLUDES:
| 500 ml | 1 Gallon | ||
| Solution A: | Xanthene Stain | Part 10521A | Part 10521B |
| Solution B: | Thiazine Stain | Part 10522A | Part 10522B |
Additionally Needed:
| Helicobacter sp., Artificial Control Slides | Part 4275 |
| Xylene, ACS | Part 1445 |
| Alcohol, Ethyl Denatured, 100% | Part 10841 |
| Alcohol, Ethyl Denatured, 95% | Part 10842 |
For storage requirements and expiration date refer to individual product labels.
APPLICATION:
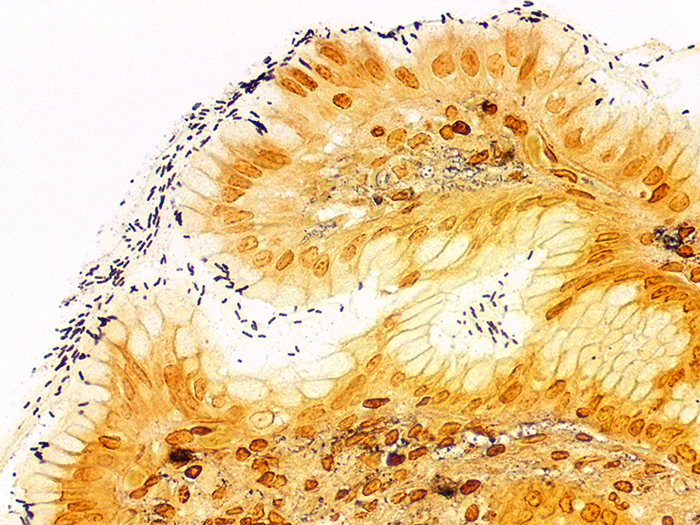
Newcomer Supply Differential Stain procedure, a modification of the Wright Giemsa Stain, provides a rapid staining method for demonstration of Helicobacter pylori sp. in gastrointestinal tissue sections. Procedures for both monochromatic and polychromatic versions of the Differential Stain are provided.
METHOD:
Fixation: Formalin 10%, Phosphate Buffered (Part 1090)
Technique: Paraffin sections cut at 4 microns
Solutions: All solutions are manufactured by Newcomer Supply, Inc.
STAINING PROCEDURE:
-
- If necessary, heat dry tissue sections/slides in oven.
- Deparaffinize sections thoroughly in three changes of xylene, 3 minutes each. Hydrate through two changes each of 100% and 95% ethyl alcohols, 10 dips each. Wash well with distilled water.
-
- Proceed with either the monochromatic or polychromatic staining method.
-
Monochromatic Staining Method: See Procedure Note #1.
-
- Place slides in Solution B: Thiazine Stain for 1-4 minutes depending upon staining intensity preference.
- Rinse quickly in distilled water to remove excess stain.
- Allow slides to air-dry in a vertical position.
- Dip dried slides in xylene and coverslip with compatible mounting medium.
-
- See Procedure Note #2.
-
RESULTS:
| Helicobacter pylori sp. | Dark blue |
| Collagen and muscle | Blue |
| Nuclei | Blue |
| Cytoplasm | Varying shades of light blue |
Polychromatic Staining Method: See Procedure Note #1.
-
- Place slides in Solution A: Xanthene Stain for 3-5 minutes.
- Drain slides briefly; go directly into Solution B: Thiazine Stain for 1-4 minutes depending upon staining intensity preference.
- Rinse well in distilled water.
- Allow slides to air-dry in a vertical position.
- Dip dried slides in xylene and coverslip with compatible mounting medium.
-
- See Procedure Note #2.
-
RESULTS:
| Helicobacter pylori sp. | Dark blue |
| Collagen and muscle | Pale pink |
| Nuclei | Blue/violet |
| Cytoplasm | Varying shades of light blue |
PROCEDURE NOTES:
-
- The timings are suggested ranges. Optimal staining times will depend upon staining intensity preference.
- The elimination of dehydration steps is necessary to retain the dark stain of the organism.
- If using a xylene substitute, closely follow the manufacturer’s recommendations for deparaffinization and coverslipping steps.
REFERENCES:
-
- Potvin, Carol. “A Modified Diff-Quik Stain for Helicobacter pylori in Gastrointestinal Biopsies.” Laboratory Medicine6 (1994): 389-391.
- Skipper, Ray, and Don DeStephano. “A Rapid Stain for Campylobacter pylori in Gastrointestinal Tissue Sections Using Diff-Quik.” The Journal of Histotechnology4 (1989): 303-304.
- Modifications developed by Newcomer Supply Laboratory.