Gram Positive & Gram Negative Bacteria, Animal
|
Validation Stain: Gram, Brown-Brenn
Other Applicable Stains: Gram, Brown-Hopps and Gram-Twort
|
Gram (+) and Gram (-) In animal tissue with specific infection or disease.
PRODUCT SPECIFICATIONS:
Tissue: Positive staining animal organ.
Fixation: Formalin 10%, Phosphate Buffered (Part 1090).
Section/Glass: Paraffin sections cut at 4 microns on Superfrost™ Plus slides.
Quality Control Stain: Brown-Brenn quality control stained slide(s) included.
Reactivity: Guaranteed product specific reactivity for one year from date of receipt. Revalidate after one year to verify continued reactivity.
Storage: 15-30°C in a light deprived and humidity controlled environment.
Intended Use: To verify histological techniques and reagent reactivity.
Before using unstained control slides, review the enclosed stained slide(s) to ensure that this tissue source is acceptable for testing needs.
CONTROL SLIDE VALIDATION:
| With Gram, Brown-Brenn Stain Kit: | Part 9123A | Individual Stain Solution | |
| Solution A: | Crystal Violet-Oxalate Stain, Alcoholic | 250 ml | Part 10422 |
| Solution B: | Iodine, Gram, Aqueous | 250 ml | Part 1140 |
| Solution C: | Acetone-Alcohol 1:1 | 250 ml | Part 10016 |
| Solution D: | Basic Fuchsin Stain 0.25%, Aqueous | 250 ml | Part 1011 |
| Solution E: | Tartrazine Stain 0.25%. Acetic Aqueous | 250 ml | Part 14016 |
APPLICATION:
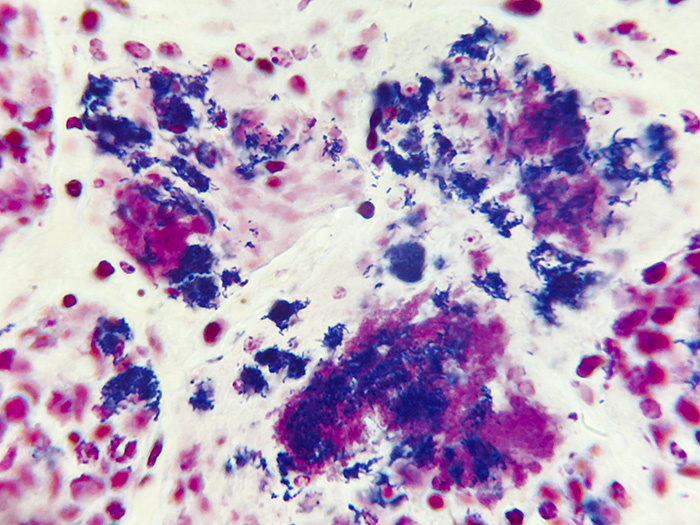
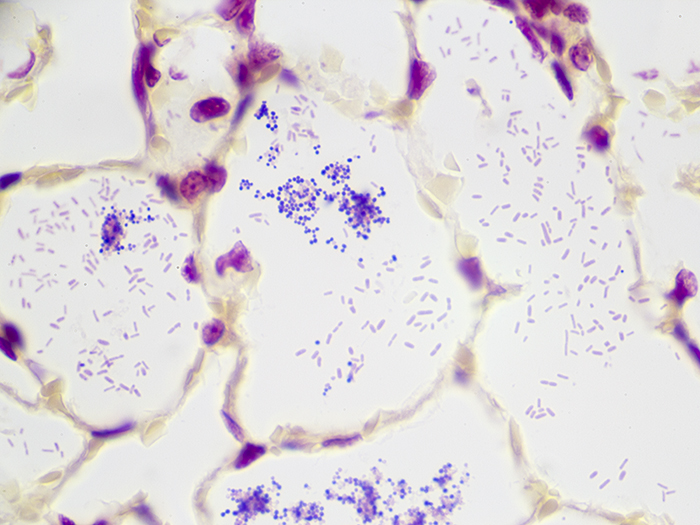
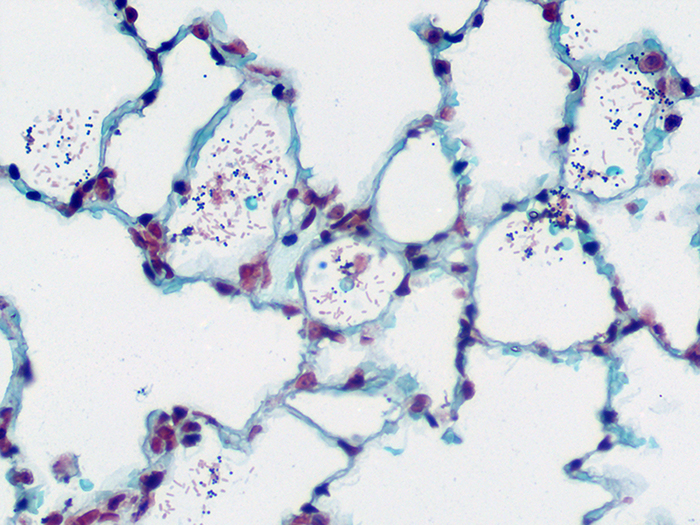
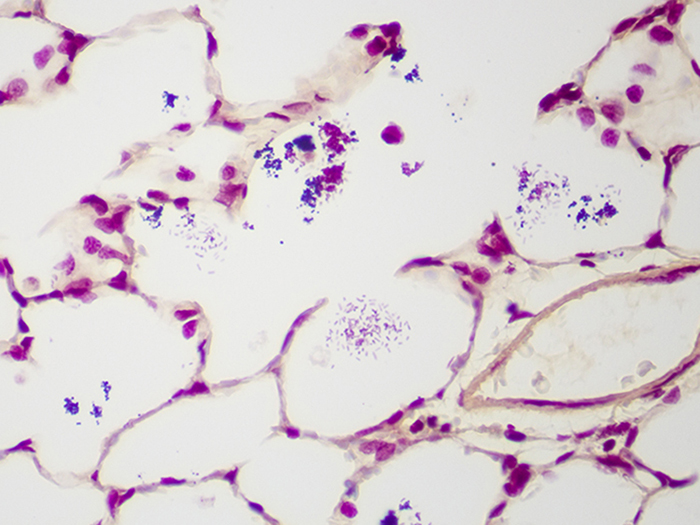
Newcomer Supply Gram Positive & Gram Negative Bacteria, Animal Control Slides are for the positive histochemical staining of gram positive and gram negative bacteria in a naturally occurring infection.
PRESTAINING PREPARATION:
-
- Heat dry sections in oven according to your laboratory protocol.
- Filter Solution A: Crystal Violet-Oxalate Stain, Alcoholic.
STAINING PROCEDURE:
-
- Deparaffinize sections thoroughly in three changes of xylene, 3 minutes each. Hydrate through two changes each of 100% and 95% ethyl alcohols, 10 dips each. Wash well with distilled water.
-
- See Procedure Notes #1 and #2.
-
- Stain in freshly filtered Solution A: Crystal Violet-Oxalate Stain, Alcoholic (Step #2) for 1 minute.
- Rinse well in distilled water.
- Mordant in Solution B: Iodine, Gram, Aqueous for 1 minute.
- Rinse well in distilled water, removing excess iodine.
- Decolorize in Solution C: Acetone-Alcohol 1:1 until blue stops running; 7-10 dips.
- Rinse well in distilled water.
- Place in Solution D: Basic Fuchsin Stain 0.25%, Aqueous for 90 seconds.
- Rinse well in distilled water.
- Dip once in Solution C: Acetone-Alcohol 1:1.
- Counterstain in Solution E: Tartrazine Stain 0.25%, Acetic Aqueous for 5-15 seconds.
- Rinse well in distilled water.
- Dehydrate in two changes of 100% ethyl alcohol, 5 dips each. Clear in three changes of xylene, 10 dips each; coverslip with compatible mounting medium.
-
- Do not use 95% alcohol in the dehydration step.
-
- Deparaffinize sections thoroughly in three changes of xylene, 3 minutes each. Hydrate through two changes each of 100% and 95% ethyl alcohols, 10 dips each. Wash well with distilled water.
RESULTS:
| Gram positive bacteria | Blue/violet |
| Gram negative bacteria | Red |
PROCEDURE NOTES:
-
- Drain slides after each step to prevent solution carry over.
- Do not allow sections to dry out at any point during procedure.
- If using a xylene substitute, follow manufacturer’s recommendation for deparaffinization and clearing steps.
REFERENCES:
-
- Bancroft, John D., and Marilyn Gamble. Theory and Practice of Histological Techniques. 6th ed. Oxford: Churchill Livingstone Elsevier, 2008. 312-313.
- Brown, J.H., and L. Brenn. “A Method for the Differential Staining of Gram Positive and Gram Negative Bacteria in Tissue Sections”.Bulletin of The Johns Hopkins2 (1931): 69-73.
- Luna, Lee G. Histopathologic Methods and Color Atlas of Special Stains and Tissue Artifacts. Gaitheresburg, MD: American Histolabs, 1992. 188-189.
- Modifications developed by Newcomer Supply Laboratory.